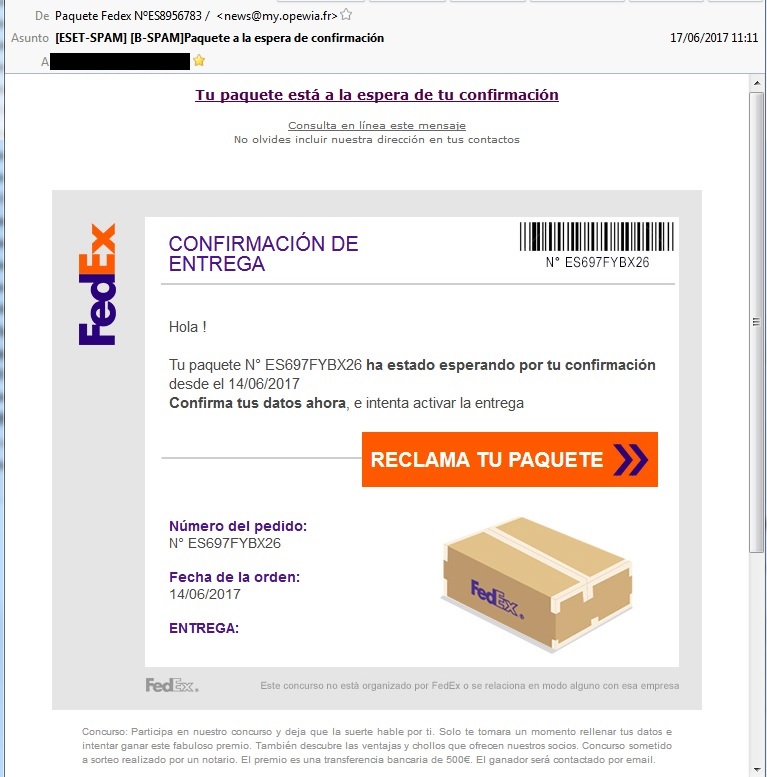
Paquete de FedEX? Ten cuidado a quien le das tus datos personales – Protegerse. Blog del laboratorio de Ontinet.com
SMS con información de un paquete retenido en Correos. Nuevo intento de estafa – Protegerse. Blog del laboratorio de Ontinet.com

16 colores planos universales establecidos para aplicaciones web y móviles análisis de datos globales enviar análisis de gráficos supermercado paquete editable de elementos de diseño de vectores creativos 18569150 Vector en Vecteezy

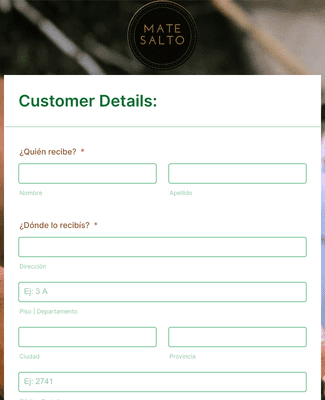
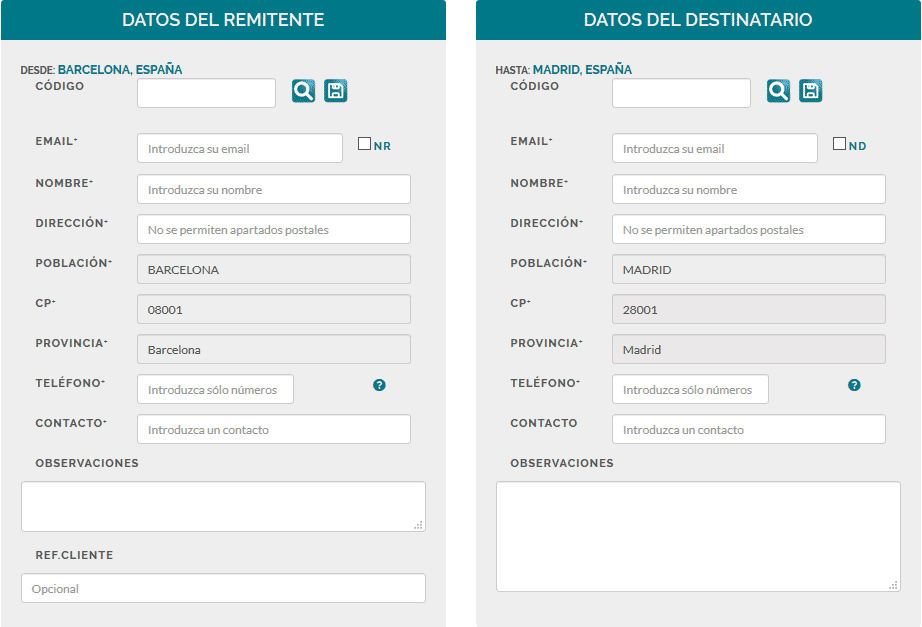
Multienvios S.A - Para que tus paquetes llegen a tiempo es muy importante completar estos datos 👆 Sii va a enviar su encomienda 📦 Poner los datos del destinatario 📝Nombre y apellido:

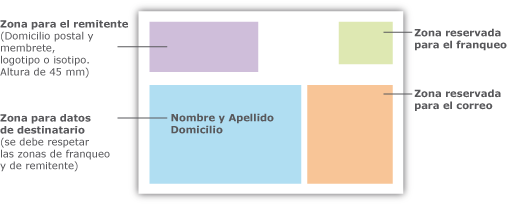
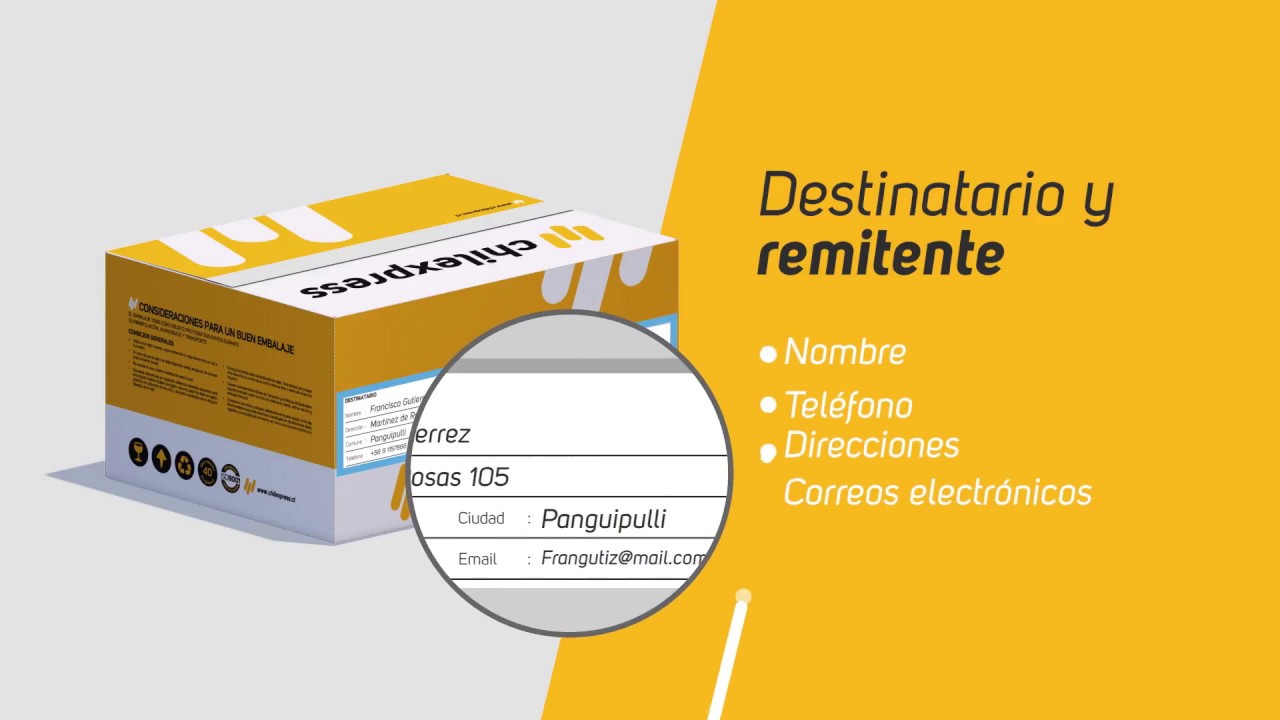
Muy importante para que tu envío viaje seguro y llegue a tiempo😉📦📨 *Recuerda seguir todas las medidas de seguridad para cuidar tu salud, nosotros lo estamos haciendo para brindarte el mejor servicio... -

Correos facilita el envío de su 'Paq Peregrino' desde ocho establecimientos navarros del Camino de Santiago